Case study - ONE WAY ISP Satellite internet
This case study reveals the easiness with which a terrestrial provider from Lebanon switched from the terrestrial 2
mbps channel which was working only at 0.5 mbps to a 0.5 mbps terrestrial channel and a 4 mbps satellite channel at the same price.
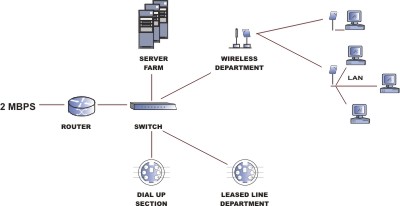
Before switching to ONE WAY ISP service
|
The technical adjustments were minimal.
The router IP on the internal interface was moved to the internal interface of the DVB router, so nothing else had to be changed.
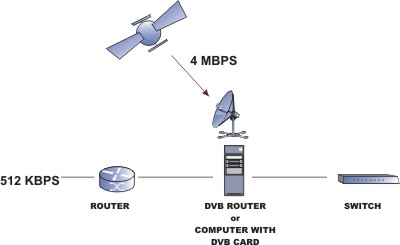
After switching to ONE WAY ISP service for incoming traffic
|
All the private IPs belonging to the customers were notified and routed through BizarNet.
Thus, the Internet knew the route through the terrestrial provider until the route was changed by Bizarnet,
so the customers were never disconnected from the Internet.
The Internet had 2 routes to reach the customers so the connection was only interrupted for a few minutes, until the DVB router was plugged in.
A small 4 IPs class allocation was necessary for the router that connected the network.
It is possible to use a normal PC instead of the DVB router, but the computer has to be fast and equipped with a DVB card.
On this computer which plays a gateway role, a firewall may be installed, but also transparent proxy, even though the Operating System is Linux or Windows.
Therefore, with a slight change and a minimum investment, that provider has totally switched it download traffic to satellite, in the same costs, but in a double bandwidth.
Its previous connection was 2 mbps but because of the weak quality of the connection, the real usage was only 1 mbps.
By switching the download traffic to the satellite, there was no need for a 2 mbps terrestrial line, but only a 0.5 mbps one.
The Satellite Service taken by the provider was 2 mbps dedicated with a burst up to 4 mbps. Therefore, it will have its own backup
bandwidth, to increase or decrease according to its business needs.
Flexibility
If the provider's business is growing, then new IPs routing could easily be performed through BizarNet, as easy as through the terrestrial provider.
Meanwhile, if the provider is not happy with its current terrestrial line, it can change it at any time, even without notifying us,
due to the flexibility of our service. Regardless the customer's location and from where he establishes the VPN connection, once the VPN
connection is online, its IP classes are routed toward it and it will receive the traffic sent to it.
So, the traffic flow occurs like this:
- The customer's request gets through several routes and ways to the DVB router, then goes to the normal router and then to the Internet through the Internet provider at which it is connected.
- When from the Internet comes back the reply, it will go to BizarNet, uploads on the satellite, downloads into the DVB router, and it will enter the provider's network and go to the source IP.
Technical details
On-line documentation
Prices
Equipment
Coverage
|